Chemokine Superfamily Pathway: Human/Mouse Ligand-Receptor Interactions
Click on one of the chemokine subfamilies shown in the Explore Pathways box below to see the specific chemokines that belong to each group, their receptors, and the different immune cell types that have been shown to express the chemokine receptors.
(A or B)
(A or B)
CRAM-A/B
CRAM-A/B
LCCR
LCCR
CCL3L3, CCL4L1, CCL4L2
M: CCL3-7, 9/10
CCL3L3, CCL4L1, CCL4L2
M: CCL3-7, 9/10
M: CCL2, 7, 12
M: CCL2, 7, 12
24, 26, 28, CCL3L1, CCL3L3
M: CCL5, 7, 9/10, 11, 24
24, 26, 28, CCL3L1, CCL3L3
M: CCL5, 7, 9/10, 11, 24
M: CCL2, 3, 5, 17, 22
M: CCL2, 3, 5, 17, 22
CCL3L3, CCL4L1, CCL4L2
M: CCL3-5
CCL3L3, CCL4L1, CCL4L2
M: CCL3-5
M: CCL20
M: CCL20
M: CCL19, 21
M: CCL19, 21
M: CCL1, 8
M: CCL1, 8
M: CCL25
M: CCL25
M: CCL27, 28
M: CCL27, 28
M: CCL19, 21, 25
M: CCL19, 21, 25
M: CCL2, 3
M: CCL2, 3
M: XCL1
M: XCL1
M: CX3CL1
M: CX3CL1
M: CXCL7, LIX
M: CXCL7, LIX
M: CXCL1-3, 7, LIX
M: CXCL1-3, 7, LIX
M: CXCL4, 9-11
M: CXCL4, 9-11
M: CXCL12
M: CXCL12
M: CXCL13
M: CXCL13
M: CXCL16
M: CXCL16
M: CXCL11, 12
M: CXCL11, 12
M: CXCL14, 17
M: CXCL14, 17
M: CCL2, 11
M: CCL2, 11
M: CXCL1, 2, LIX
M: CXCL1, 2, LIX
| Receptor | Immune Cell Expression |
|---|---|
| XCR1 | B Cells, Dendritic Cells, Natural Killer Cells, Neutrophils, T Cells |
| Receptor | Immune Cell Expression |
|---|---|
| CCR1 | Dendritic Cells, Eosinophils, Monocytes, Natural Killer Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CCR2 (A or B) | Basophils, Immature Dendritic Cells, Monocytes, Natural Killer Cells, Memory T Cells, Activated T Cells |
| CCR3 | Basophils, Eosinophils, Mast Cells, Monocytes, Platelets, Th2 Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CCR4 | Basophils, Dendritic Cells, Eosinophils, Macrophages, Monocytes, Platelets, gamma delta T Cells, Regulatory T Cells, Th2 Cells, Th17 Cells, Th22 Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CCR5 | Dendritic Cells, Monocytes, Natural Killer Cells, Th1 Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CCR6 | B Cells, Dendritic Cells, Lymphoid Tissue-inducer Cells, gamma delta T Cells, Th17 Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CCR7 | B Cells, Dendritic Cells, Neutrophils, Naïve T Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CCR8 | Dendritic Cells, Eosinophils, Monocytes, Regulatory T Cells, Th2 Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CCR9 | Macrophages, Monocytes, Plasma Cells, Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CCR10 | Plasma Cells, Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells, gamma delta T Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CCR11 | Not yet shown |
| CCRL2/CRAM-A/B | B Cells, Dendritic Cells, Monocytes, Natural Killer Cells, Neutrophils, T Cells |
| CCRL2/LCCR | Dendritic Cells, Macrophages, Mast Cells |
| D6 | B Cells, Dendritic Cells, Monocytes |
| DARC | Not yet shown |
| PITPNM3 | Not yet shown |
| Human CCL26 has also been shown to bind CX3CR1 |
| Receptor | Immune Cell Expression |
|---|---|
| CXCR1 | Granulocytes, Mast Cells, Monocytes, CD56+, Natural Killer Cells, Neutrophils, CD8+ T Cells |
| CXCR2 | Granulocytes, Mast Cells, Monocytes, CD56+, Natural Killer Cells, Neutrophils, CD8+ T Cells |
| DARC | Not yet shown |
| Receptor | Immune Cell Expression |
|---|---|
| CXCR3 | Activated B Cells, Kupffer Cells, Mast Cells, Activated Natural Killer Cells, CD8+ T Cells, Th1 Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CXCR3B | Not yet shown |
| CXCR4 | B Cells, Basophils, Dendritic Cells, Eosinophils, Mast Cells, Monocytes, Natural Killer Cells, Neutrophils, Naïve T Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CXCR5 | B Cells, Dendritic Cells, gamma delta T Cells, Follicular Helper T Cells |
| CXCR6 | Natural Killer Cells, Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils, CD8+ T Cells, Memory T Cells |
| CXCR7 | B Cells, Monocytes, Neutrophils |
| DARC | Not yet shown |
| Receptor | Immune Cell Expression |
|---|---|
| CX3CR1 | Macrophages, Monocytes, Natural Killer Cells, Platelets, Memory T Cells |
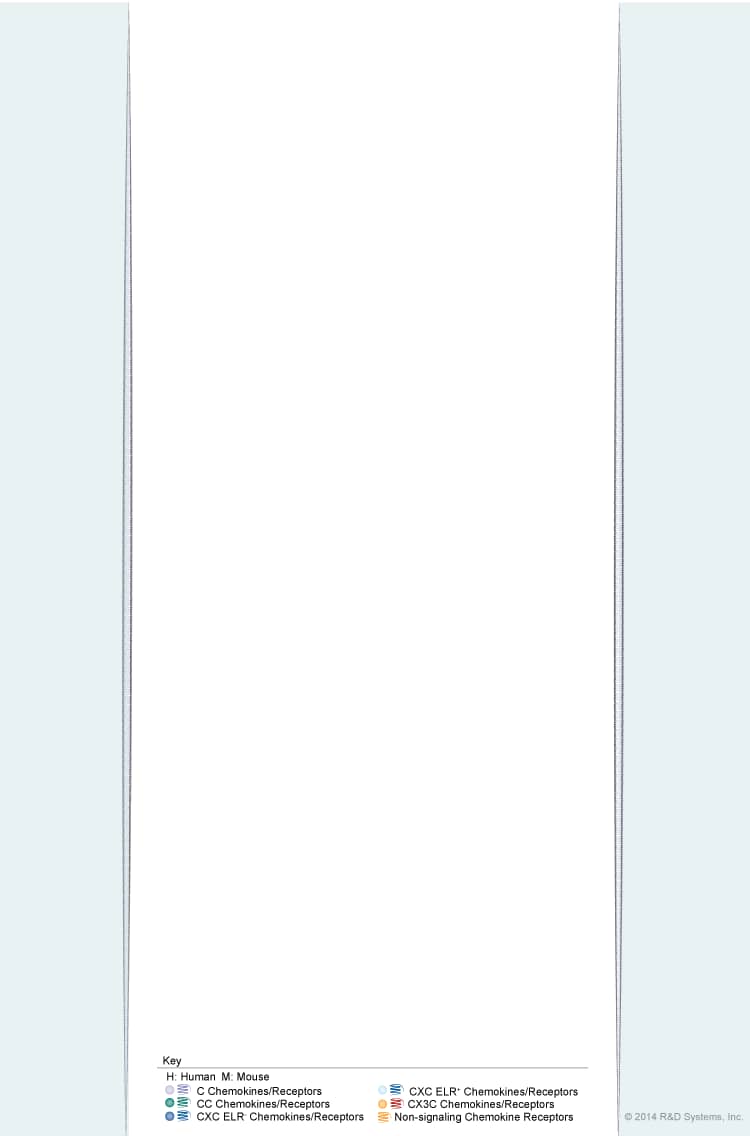
Overview of Chemokine Superfamily: Human/Mouse Ligand-Receptor Interactions
Chemokines are small cell surface-localized or secreted chemotactic cytokines that bind to and activate specific G protein-coupled chemokine receptors. Most chemokines have at least four conserved N-terminal cysteine residues that form two intramolecular disulfide bonds. Four chemokine subfamilies (CXC, CC, C, and CX3C) have been defined based upon the placement of the first two cysteine residues. The CXC chemokine subfamily is characterized by two cysteine residues separated by one amino acid. Within this subfamily, two CXC classes are further defined by the presence or absence of an ELR motif sequence. ELR- CXC chemokines act as chemoattractants for lymphocytes, while ELR+ CXC chemokines are chemoattractants for neutrophils. Additionally, CXC chemokines can mediate angiogenesis. The CC chemokine subfamily is defined by two adjacent cysteine residues. CC chemokines induce inflammatory responses via regulation of monocyte, macrophage, mast cell, and T cell migration. C chemokines are characterized by a single cysteine residue and are constitutively expressed in the thymus where they regulate T cell differentiation. The CX3C chemokine subfamily is defined by two cysteine residues separated by three amino acids. Cell surface-localized CX3CL1/Fractalkine mediates leukocyte adhesion, while soluble CX3CL1/Fractalkine is chemotactic for leukocytes. CX3CL1/Fractalkine is also a critical regulator of microglia-neuron communication during neural development.
While chemokine receptors generally bind only one subfamily of chemokines, within those subfamilies, most chemokines display promiscuous receptor binding patterns. The redundancy of chemokine ligand-receptor binding may ensure robust signaling. In addition, promiscuous binding and non-signaling chemokine receptors offer mechanisms by which chemokine signaling can be regulated by either subtle differences in receptor signaling or differences in ligand-receptor expression patterns. Select chemokine ligands and receptors are implicated in HIV infection and persistence, while aberrant chemokine expression and signaling is associated with pathological conditions including inflammatory diseases and cancer.
To learn more, please visit our Chemokines and Receptors Research Area.
Get Print Copy of this Pathway


